本文解释8086机器开机后的过程,和linux0.11中的相关源代码文件:linux-0.11\boot 目录下的 bootsect.s, setup.s 和 head.s
开机后BIOS的工作
80×86结构的计算机打开电源后,CPU自动进入实模式,并从地址0xFFFF0处执行代码。这个地址正是ROM-BIOS的地址。BIOS会完成系统的检测的相关动作,并在地址0处初始化BIOS中断向量。然后,它会把可启动设备的引导扇区(第一个扇区,512字节)读入内存绝对地址0x7C00处,然后跳转到这个地方并执行此处的代码。
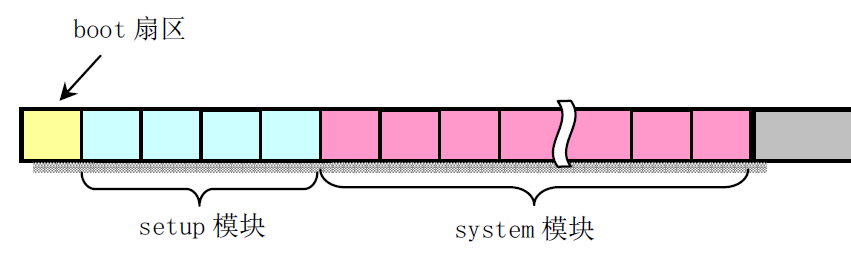
bootsect.s
bootsect.s也就是引导程序,它位于磁盘的第一个扇区512字节中。在磁盘中它的后面是setup.s编译后的setup模块,在后面是system模块
在BIOS把bootsect模块加载到0x7C00处后,CPU会从此处执行。bootsect完成的主要功能为
1. 把自己从内存中0x7C00处移动到0x90000处,同时CPU跳转到挪动后的位置继续执行
2. 使用BIOS 0x13中断,把setup模块读入内存0x90200处
3. 使用BIOS 0x10中断,在屏幕上显示”Loading system…”
4. 使用BIOS 0x13中断, 把system模块读入内存0x10000处
1. 移动到0x90000
SETUPLEN = 4 ! nr of setup-sectors BOOTSEG = 0x07c0 ! original address of boot-sector INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! setup starts here SYSSEG = 0x1000 ! system loaded at 0x10000 (65536). ENDSEG = SYSSEG + SYSSIZE ! where to stop loading ! ROOT_DEV: 0x000 - same type of floppy as boot. ! 0x301 - first partition on first drive etc ROOT_DEV = 0x306 entry _start _start: mov ax,#BOOTSEG mov ds,ax mov ax,#INITSEG mov es,ax mov cx,#256 sub si,si sub di,di rep movw jmpi go,INITSEG go: mov ax,cs
此段代码把内存 0x7C00处的512字节内容移动到内存0x90000处
ds = 0x07c0 , es = 0x9000, si = 0, di = 0
rep movw 的作用是 将 DS:SI 的内容送至 ES:DI ,每次移动1个字(2字节),移动cx=256次
注意寻址方式, ds:si 实际的地址是ds左移4位,加上si,正好是0x07c00
复制过后,jmpi语句跳转过去,正好接着执行go处的语句
2. 加载setup模块
go: mov ax,cs mov ds,ax mov es,ax ! put stack at 0x9ff00. mov ss,ax mov sp,#0xFF00 ! arbitrary value >>512 ! load the setup-sectors directly after the bootblock. ! Note that 'es' is already set up. load_setup: mov dx,#0x0000 ! drive 0, head 0 mov cx,#0x0002 ! sector 2, track 0 mov bx,#0x0200 ! address = 512, in INITSEG mov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN ! service 2, nr of sectors int 0x13 ! read it jnc ok_load_setup ! ok - continue mov dx,#0x0000 mov ax,#0x0000 ! reset the diskette int 0x13 j load_setup
跳转过来后,cs = 0x9000 ,首先把这个段地址赋值给ds, es 和ss,设置 sp=0xFF00,也就是堆栈地址从ss:sp = 0x9ff00处开始。
load_setup完成读setup的工作,使用BIOS 0x13号中断,之前设置寄存器ax, bx, cx, dx作为传入的参数:
| 寄存器 | 值 | 说明 |
| AH | 2 | 功能号,2表示读取扇区功能 |
| AL | SETUPLEN=4 | 需要读取的扇区数量 |
| CH | 0 | 磁道号的低8位 |
| CL | 2 | 0-5位是从哪个扇区开始读,6-7位是磁道号的高2位 |
| DH | 0 | 磁头号 |
| DL | 0 | 驱动器号 |
| ES:BX | 9000:0200 | 把扇区的内容读到ES:BX(90200)的位置 |
如果出错,标志寄存器CF置位,AH中存放出错码
如果出错要0x13中断的0号功能复位驱动器
| 寄存器 | 值 | 说明 |
| AH | 0 | 功能号,0表示复位驱动器 |
| DL | 0 | 需要复位的驱动器编号 |
3. 显示Loading文字
! Print some inane message mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos xor bh,bh int 0x10 mov cx,#24 mov bx,#0x0007 ! page 0, attribute 7 (normal) mov bp,#msg1 mov ax,#0x1301 ! write string, move cursor int 0x10 msg1: .byte 13,10 .ascii "Loading system ..." .byte 13,10,13,10
用到0x10中断的两个功能 0x03功能读光标位置,0x13功能显示字符串
AH = 0x03 读光标, bh=0表示页号,返回值CH=光标起始行,DH=行,DL=列
AH 0x13 显示字符,参数:
| AL | 显示模式 |
| BH | 视频页 |
| BL | 属性值,当AL=0和1时有用 |
| CX | 字符串长度 |
| DH,DL | 屏幕上显示起始位置行,列 |
| ES:BP | 字符串的地址 |
显示模式(AL):
0x00:字符串只包含字符码,显示之后不更新光标位置,属性值在BL中
0x01:字符串只包含字符码,显示之后更新光标位置,属性值在BL中
0x02:字符串包含字符码及属性值,显示之后不更新光标位置
0x03:字符串包含字符码及属性值,显示之后更新光标位置
4. 加载system,跳转到setup
... call read_it ... jmpi 0,SETUPSEG
setup.s
1. 通过 BOIS 获取系统数据,保存到0x90000开始的位置,供后续system模块使用
2. 把system模块从0x10000的移到0x0000开始的地方
3. 加载中断描述符表寄存器和全局描述符表寄存器,开启A20地址线
4. 重新设置两个中断控制芯片
5. 设置CPU的CR0寄存器,进入32位保护模式,并且跳转到system模块最前面部分的head.s程序运行
1. 获取系统数据
INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way entry start start: ! ok, the read went well so we get current cursor position and save it for ! posterity. mov ax,#INITSEG ! this is done in bootsect already, but... mov ds,ax mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos xor bh,bh int 0x10 ! save it in known place, con_init fetches mov [0],dx ! it from 0x90000. ! Get memory size (extended mem, kB) mov ah,#0x88 int 0x15 mov [2],ax ...
通过一些BIOS功能调用读取硬件参数,放入0x90000处:
| 内存地址 | 长度 | 名称 |
| 0x90000 | 2 | 光标位置 |
| 0x90002 | 2 | 扩展内存数 |
| … | ||
| 0x901FC | 2 | 跟设备号 |
2. 移动system模块
把system从0x10000处移动到 0 地址处。
! first we move the system to it's rightful place mov ax,#0x0000 cld ! 'direction'=0, movs moves forward do_move: mov es,ax ! destination segment add ax,#0x1000 cmp ax,#0x9000 jz end_move mov ds,ax ! source segment sub di,di sub si,si mov cx,#0x8000 rep movsw jmp do_move
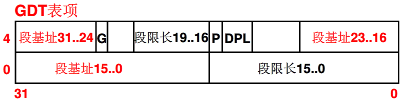
3. 设置临时的GDT表和LDT表
! then we load the segment descriptors end_move: mov ax,#SETUPSEG ! right, forgot this at first. didn't work :-) mov ds,ax lidt idt_48 ! load idt with 0,0 lgdt gdt_48 ! load gdt with whatever appropriate ! that was painless, now we enable A20 call empty_8042 mov al,#0xD1 ! command write out #0x64,al call empty_8042 mov al,#0xDF ! A20 on out #0x60,al call empty_8042 gdt: .word 0,0,0,0 ! dummy .word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb) .word 0x0000 ! base address=0 .word 0x9A00 ! code read/exec .word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386 .word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb) .word 0x0000 ! base address=0 .word 0x9200 ! data read/write .word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386 idt_48: .word 0 ! idt limit=0 .word 0,0 ! idt base=0L gdt_48: .word 0x800 ! gdt limit=2048, 256 GDT entries .word 512+gdt,0x9 ! gdt base = 0X9xxxx
此处设置GDT表,为了后面jmpi 0,8 指令可以正确跳转到物理0地址
4. 设置中断控制芯片
5. 进入保护模式,跳转到head.s
mov ax,#0x0001 ! protected mode (PE) bit lmsw ax ! This is it! jmpi 0,8 ! jmp offset 0 of segment 8 (cs)
lmsw会设置cr0寄存器的值,cr0的第1位为PE位,设置为1启动保护模式。
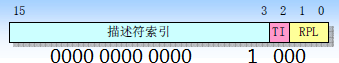
jmpi 0,8 就成了保护模式下的跳转, 8其实成了段选择符,要用二进制来理解:
是选择GDT的第1个表项,GDT表在第3步中设置了内容:
第0项
.word 0,0,0,0 ! dummy
第1项
.word 0x07FF ! 8Mb – limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb)
.word 0x0000 ! base address=0
.word 0x9A00 ! code read/exec
.word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386
head.s
head.s在system的最开始处,完成保护模式的一些初始化工作,然后调用main.c中的main函数
1. 初始化
startup_32: movl $0x10,%eax mov %ax,%ds mov %ax,%es mov %ax,%fs mov %ax,%gs lss stack_start,%esp call setup_idt call setup_gdt movl $0x10,%eax # reload all the segment registers mov %ax,%ds # after changing gdt. CS was already mov %ax,%es # reloaded in 'setup_gdt' mov %ax,%fs mov %ax,%gs lss stack_start,%esp xorl %eax,%eax 1: incl %eax # check that A20 really IS enabled movl %eax,0x000000 # loop forever if it isn't cmpl %eax,0x100000 je 1b /* * NOTE! 486 should set bit 16, to check for write-protect in supervisor * mode. Then it would be unnecessary with the "verify_area()"-calls. * 486 users probably want to set the NE (#5) bit also, so as to use * int 16 for math errors. */ movl %cr0,%eax # check math chip andl $0x80000011,%eax # Save PG,PE,ET /* "orl $0x10020,%eax" here for 486 might be good */ orl $2,%eax # set MP movl %eax,%cr0 call check_x87 jmp after_page_tables
2. 跳转到main函数
after_page_tables:
pushl $0 # These are the parameters to main :-)
pushl $0
pushl $0
pushl $L6 # return address for main, if it decides to.
pushl $main
jmp setup_paging
L6:
jmp L6 # main should never return here, but
# just in case, we know what happens.
setup_paging:
.....
ret /* this also flushes prefetch-queue */
init/main.c
void main(void) /* This really IS void, no error here. */
{ /* The startup routine assumes (well, ...) this */
/*
* Interrupts are still disabled. Do necessary setups, then
* enable them
*/
......
mem_init(main_memory_start,memory_end);
trap_init();
blk_dev_init();
chr_dev_init();
tty_init();
time_init();
sched_init();
buffer_init(buffer_memory_end);
hd_init();
floppy_init();
sti();
move_to_user_mode();
if (!fork()) { /* we count on this going ok */
init();
}
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏