要求:
掌握添加设备驱动程序的方法
内容
采用模块方法,添加一个新的字符设备的驱动程序,实现打开/关闭、读/写等基本操作
编写一个应用程序,测试添加的驱动程序
如果打开设备失败,应该用root身份来运行。下面的示例全部是root用户的身份。
一、编写驱动程序源代码lgsDrive.c
源代码如下:
#include "linux/kernel.h"
#include "linux/module.h"
#include "linux/fs.h"
#include "linux/init.h"
#include "linux/types.h"
#include "linux/errno.h"
#include "linux/uaccess.h"
#include "linux/kdev_t.h"
#define MAX_SIZE 1024
int my_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file);
int my_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file);
ssize_t my_read(struct file *file, char __user *user, size_t t, loff_t *f);
ssize_t my_write(struct file *file, const char __user *user, size_t t, loff_t *f);
char message[MAX_SIZE] = "this is a origin message";
int device_num;//设备号
char* devName = "lgsDrive";//设备名
struct file_operations pStruct =
{
open:my_open,
release:my_release,
read:my_read,
write:my_write,
};
/* 注册 */
int init_module()
{
int ret;
ret = register_chrdev(0, devName, &pStruct);
if (ret < 0)
{
printk("failed to register_chrdev.\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
printk("the lgsDrive has been registered!\n");
printk("id: %d\n", ret);
device_num = ret;
return 0;
}
}
//注销
void cleanup_module()
{
unregister_chrdev(device_num, devName);
printk("unregister successful.\n");
}
//打开
int my_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("open lgsDrive OK!\n");
try_module_get(THIS_MODULE);
return 0;
}
//关闭
int my_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("Device released!\n");
module_put(THIS_MODULE);
return 0;
}
//读设备里的信息
ssize_t my_read(struct file *file, char __user *user, size_t t, loff_t *f)
{
if(copy_to_user(user,message,sizeof(message)))
{
return -2;
}
return sizeof(message);
}
//向设备里写信息
ssize_t my_write(struct file *file, const char __user *user, size_t t, loff_t *f)
{
if(copy_from_user(message,user,sizeof(message)))
{
return -3;
}
return sizeof(message);
}
二、编写Makefile
内容如下
obj-m := lgsDrive.o
PWD := $(shell pwd)
KERNELDIR := /usr/src/linux-3.12.38
all:
make -C $(KERNELDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
.PHONY: clean
clean:
rm -rf *.o *~ core *.ko *.mod.c modules.order Module.symvers
第一行 obj-m := lgsDrive.o是指定模块名称是lgsDrive.ko
第二行定义变量PWD为当前目录
第三行=后面应该是你的linux源代码所在的文件夹。这次编译模块要用到linux源代码中的makefile 。
第5行的意思是,进入KERNELDIR (也就是linux源代码)文件夹,使用那里的makefile并执行make modules 。M=$(PWD)的作用是回到原来的目录。
第8行说明clean是伪目标文件,可以省略。只有显式 使用make clean 才会执行第9行命令,作用是删除中间文件。
三、编译驱动程序
使用root用户,运行命令
make
编译驱动程序。完成后可以使用ls命令查看,可以发现生成的lgsDrive.ko文件。这就是我们的驱动程序。
四、装载模块
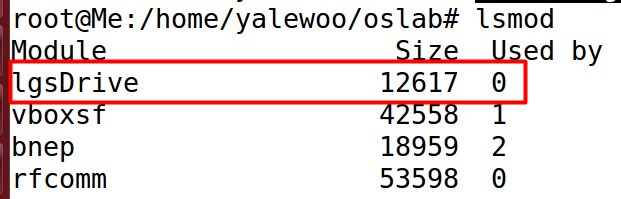
使用命令lsmod可以查看当前已经有的模块。
使用下面的命令装载我们自己的模块
insmod lgsDrive.ko
然后再次lsmod可以找到新加入的模块
这时候使用dmesg命令。可以查看源代码lgsDrive.c中,设备注册函数init_module()中的prink的输出
[ 6639.570322] the lgsDrive has been registered!
[ 6639.570328] id: 250
五、分配设备号
使用命令ls /dev可以查看当前已有的设备。
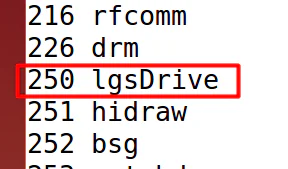
要加入自己的设备需要知道主设备号,在第四步的dmesg中可以找到输出的id:250 设备号(驱动源代码43行的输出)。也可以使用命令
cat /proc/devices
查看所有设备
然后使用命令加入自己的设备:(lgsDevice是自己起的设备名字,和test.c里面的对应)
mknod /dev/lgsDevice c 250 0
然后使用 ls /dev就可以看到自己的设备了
c是指字符设备
250是主设备号(选择驱动程序)
0是指定从设备号(选择设备)这里可以随便指定
六、编写测试程序test.c
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 1024
int main(void)
{
int fd;
char buf[MAX_SIZE]; //缓冲区
char get[MAX_SIZE]; //要写入的信息
char dir[50] = "/dev/lgsDevice";
fd = open(dir, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
if (fd != -1)
{
//读初始信息
read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("%s\n", buf);
//写信息
printf("input :");
gets(get);
write(fd, get, sizeof(get));
//读刚才写的信息
read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("device Message: %s\n", buf);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
else
{
printf("Device open failed\n");
return -1;
}
}
然后使用下面的命令编译
gcc test.c -o test
然后运行 ./test
七、删除设备和模块
rm /dev/lgsDevice rmmod lgsDrive

 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏
进行make操作时提示遇到NUL字符
可以解释一下基于内核缓冲区和基于键盘缓冲区添加驱动程序的区别吗?
请问为什么我在运行的时候能向设备里写用户输入的信息,但是读不出来呢?
我是物联网班最帅的男人,外号华科吴彦祖
帮大忙了
写的真好
lgsDrive.c和Makefile在哪里创建?
直接在桌面创建就可以吗?
是的 随便一个目录就行