Given a string containing just the characters ‘(‘ and ‘)’, find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.
For “(()”, the longest valid parentheses substring is “()”, which has length = 2.
Another example is “)()())”, where the longest valid parentheses substring is “()()”, which has length = 4.
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
}
};
方法1:动态规划
用dp[i]表示以字符s[i]结尾的最长匹配的长度。
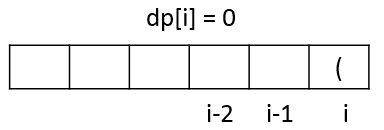
当s[i]等于'(‘时,以 ‘(‘ 结尾的字串必定不是有效的括号匹配,因此此时 dp[i]=0.
s[i]等于’)’时,要看s[i-1]。
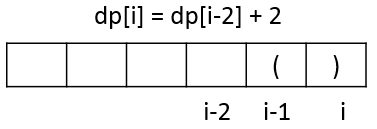
如果s[i-1]是'(‘,正好和s[i]匹配,这时,dp[i]的值就等于dp[i-2]+2
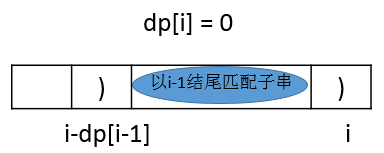
如果s[i-1]是’)’ ,这时要看以i-1结束的字串的前一个字符和s[i]是不是匹配:
情况一:i-1结束子串的前一个字符是右括号,和s[i]不匹配,此时dp[i]=0
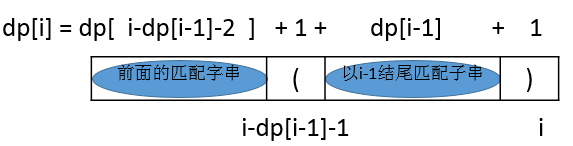
情况二:是左括号,正好匹配。
下面是代码,在s最前面加上’)’是为了上面i-2和i-dp[i-1]-2不会越界,并且不影响最后结果。
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
if (s.size() <= 1)
return 0;
s = ')' + s;
int len = s.size();
int * dp = new int[len];
int res = 0;
dp[0] = 0;
dp[1] = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < len; ++i)
{
if (s[i] == '(')
dp[i] = 0;
else
{
if (s[i-1] == '(')
dp[i] = dp[i-2] + 2;
else
{
if (s[i-dp[i-1]-1] == '(')
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + 2 + dp[ i-dp[i-1]-2 ];
else
dp[i] = 0;
}
}
res = max(res, dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
};
方法2:栈
首先用一个变量start记录上次匹配失败的位置,初始为-1 。
用一个栈stk,遇到左括号,把其下标入栈。
遇到右括号,
1. 若栈为空,则不匹配了,更新start的值。
2. 若栈不为空,弹出一个元素,和右括号匹配。
此时再看栈,如果
2.1 栈为空,则目前形成了匹配的序列,长度为 i – start
2.2 栈不为空,右括号和弹出的元素匹配了,长度为 i- stk.top()
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
if (s.size() <= 1)
return 0;
stack<int> stk;
int start = -1;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
{
if (s[i] == '(')
{
stk.push(i);
}
else
{
if (stk.empty())
{
start = i;
}
else
{
stk.pop();
if (stk.empty())
{
res = max(res, i-start);
}
else
{
res = max(res,i-stk.top());
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏