《机器学习实战》第三章中使用python画决策树
plotNode
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="sawtooth", fc="0.8")
leafNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="0.8")
arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-")
def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType):
createPlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction',
xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction',
va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args )
def createPlot():
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor="white")
fig.clf()
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False)
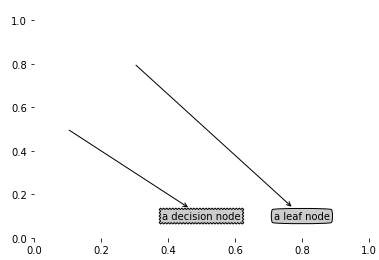
plotNode('a decision node', (0.5,0.1), (0.1,0.5), decisionNode)
plotNode('a leaf node', (0.8, 0.1),(0.3,0.8), leafNode)
plt.show()
createPlot()
plotNode的功能是画结点和线,箭头是从 parentPt 指向 centerPt 的
plotMidText
该函数用于在线的中间写入数字
def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString):
xMid = (parentPt[0]-cntrPt[0])/2.0 + cntrPt[0]
yMid = (parentPt[1]-cntrPt[1])/2.0 + cntrPt[1]
createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30)
plotTree 和 createPlot
def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt):#if the first key tells you what feat was split on
numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) #this determines the x width of this tree
depth = getTreeDepth(myTree)
firstStr = myTree.keys()[0] #the text label for this node should be this
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt)
plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode)
secondDict = myTree[firstStr]
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0/plotTree.totalD
for key in secondDict.keys():
if type(secondDict[key]).__name__=='dict':
plotTree(secondDict[key],cntrPt,str(key)) #recursion
else: #it's a leaf node print the leaf node
plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalW
plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode)
plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key))
plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0/plotTree.totalD
#if you do get a dictonary you know it's a tree, and the first element will be another dict
def createPlot(inTree):
fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white')
fig.clf()
axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[])
createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) #no ticks
#createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False) #ticks for demo puropses
plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree))
plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree))
plotTree.xOff = -0.5/plotTree.totalW; plotTree.yOff = 1.0;
plotTree(inTree, (0.5,1.0), '')
plt.show()
xOff
xOff和yOff用来记录当前要画的叶子结点的位置。
画布的范围x轴和y轴都是0到1,我们希望所有的叶子结点平均分布在x轴上。totalW记录叶子结点的个数,那么 1/totalW 正好是每个叶子结点的宽度
如果叶子结点的坐标是 1/totalW , 2/totalW, 3/totalW, …, 1 的话,就正好在宽度的最右边,为了让坐标在宽度的中间,需要减去0.5 / totalW 。所以createPlot函数中,初始化 plotTree.xOff 的值为-0.5/plotTree.totalW。这样每次 xOff + 1/totalW ,正好是下1个结点的准确位置
yOff
yOff的初始值为1,每向下递归一次,这个值减去 1 / totalD
cntrPt
cntrPt用来记录当前要画的树的树根的结点位置
在plotTree函数中,它是这样计算的
cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff)
numLeafs记录当前的树中叶子结点个数。我们希望树根在这些所有叶子节点的中间。
plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs))/2.0/plotTree.totalW
这里的 1.0 + numLeafs 需要拆开来理解,也就是
plotTree.xOff + float(numLeafs)/2.0/plotTree.totalW +1.0/2.0/plotTree.totalW
plotTree.xOff + 1/2 * float(numLeafs)/plotTree.totalW + 0.5/plotTree.totalW
因为xOff的初始值是-0.5/plotTree.totalW ,是往左偏了0.5/plotTree.tatalW 的,这里正好加回去。这样cntrPt记录的x坐标正好是所有叶子结点的中心点
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏