最新版完整代码:https://github.com/yalewoo/cpp-data-structure
二叉树
本文中的二叉树结点包含父指针,左右孩子指针,结点高度信息,具体数据结构为
//二叉树结点数据结构
template <typename T>
class BinNode
{
public:
T data; //该结点具体数据
BinNodePosi(T) parent; //父节点指针
BinNodePosi(T) lchild; //左孩子指针
BinNodePosi(T) rchild; //右孩子指针
enum RB_COLOR color; //颜色 在红黑树中使用
int height; //记录该结点高度
int horizontal_position; //记录中序遍历下该结点的序号,用于display显示
int distance_to_root; //记录到根节点的距离 用于display显示
int size(); //计算以该结点为根的二叉树结点个数(递归算法)
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsLC(T const &); //插入左孩子
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsRC(T const &); //插入右孩子
BinNodePosi(T) succ(); //返回中序遍历时该结点的后继指针
//遍历算法
template <typename VST> void travPre_R(VST &); //先序遍历递归算法
template <typename VST> void travPre_I(VST &); //先序遍历基于栈的算法1
template <typename VST> void travPre_II(VST &); //先序遍历基于栈的算法2
template <typename VST> void travIn_R(VST &); //中序遍历递归算法
template <typename VST> void travIn_I(VST &); //中序遍历基于栈的算法
template <typename VST> void travPost_R(VST &); //后序遍历递归算法
template <typename VST> void travPost_I(VST &); //后序遍历基于栈的算法
template <typename VST> void travLevel(VST &); //层次遍历 基于队列
BinNode(T e, BinNodePosi(T) p); //构造二叉树,父节点p,节点内容e
BinNode();
virtual ~BinNode(){}
};
二叉树的数据结构
//二叉树数据结构
template <typename T> class BinTree
{
protected:
int _size; //记录该二叉树结点个数
BinNodePosi(T) _root; //二叉树树根节点指针
virtual int updateHeight(BinNodePosi(T) x); //更新结点x的高度
void updateHeightAbove(BinNodePosi(T) x); //更新x以及x的所有祖先元素的高度
void updateDistanceToRoot(BinNodePosi(T) x); //更新x结点及其孩子距离根节点的距离
void calculatePosition(); //计算结点位置 结果存放在每个结点的horizontal_position和distance_to_root中
BinNodePosi(T) siblingOf(BinNodePosi(T) x); //返回结点x的兄弟结点
public:
BinTree(BinNodePosi(T) root);
BinTree();
virtual ~BinTree();
int size() const { return _size; } //返回树中结点个数
int height() const { return _root ? _root->height : 0; } //返回树的高度
bool empty() const { return !_root; } //判断树是否为空树
BinNodePosi(T) root() const { return _root; } //返回根节点指针
//拓扑连接
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsLC(BinNodePosi(T) x, T const & e); //把e作为x的左孩子插入
BinNodePosi(T) insertAsRC(BinNodePosi(T) x, T const & e); //把e作为x的右孩子插入
BinNodePosi(T) attachAsLC(BinNodePosi(T) x, BinTree<T>* & S); //把S作为x的左子树插入
BinNodePosi(T) attachAsRC(BinNodePosi(T) x, BinTree<T>* & S); //把S作为x的右子树插入
//删除x结点
virtual int remove(BinNodePosi(T) x);
//将以x为根的子树从树中删去
BinNodePosi(T) secede(BinNodePosi(T) x);
//树的遍历算法
template <typename VST> void travPre(VST &v) { _root->travPre_I(v); } //先序遍历 对每个节点执行v
template <typename VST> void travIn(VST &v) { _root->travIn_I(v); } //中序遍历
template <typename VST> void travPost(VST &v) { _root->travPost_I(v); } //后序遍历
template <typename VST> void travLevel(VST &v) { _root->travLevel_I(v); } //层次遍历
//命令行直观显示二叉树
void display();
};
下面简单介绍一些重要接口的实现思路
高度
二叉树结点自身含有height成员变量,用于记录结点的高度信息,该信息在插入和删除时进行实时维护,主要通过updateHeightAbove函数来进行更新,该函数从下到上依次调用updateHeight函数对每个结点的高度进行更新。
在插入或者删除元素后,只会影响操作元素的祖先元素的高度,其余元素高度不受影响。采用从下到上的顺序,可以保证更新x结点高度时,x的孩子的高度已经得到更新。
#define stature(p) ((p) ? (p)->height : -1) //该结点的高度 空节点高度为-1
//更新x结点的高度
template <typename T>
int BinTree<T>::updateHeight(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
return x->height = 1 + max(stature(x->lchild), stature(x->rchild));
}
//更新x及其祖先结点高度
template <typename T>
void BinTree<T>::updateHeightAbove(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
while (x)
{
updateHeight(x);
x = x->parent;
}
}
结点个数
结点个数并不是直接记录在变量中,而是每次进行计算。计算采用递归的方法,结点个数 = 左子树结点个数 + 右孩子结点个数 + 1 ,递归基是叶子结点个数为1
/*
返回该结点为根的子树的结点个数
递归求解 return lc->size() + rc->size() + 1
叶子节点 return 1
*/
template <typename T>
int BinNode<T>::size()
{
int s = 1;
if (lchild) s += lchild->size();
if (rchild) s += rchild->size();
return s;
}
树的结点操作
有插入左孩子,右孩子,左子树,右子树,分离子树,删除子树。
分离子树secede把子树从二叉树中分离,并返回子树的指针。
删除子树直接删除子树,并释放空间,返回的是删除的结点个数。
//分离子树 返回子树的树根
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BinTree<T>::secede(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
if (x->parent->lchild == x) x->parent->lchild = NULL;
if (x->parent->rchild == x) x->parent->rchild = NULL;
updateHeightAbove(x->parent);
BinTree<T> * S = new BinTree<T>;
S->_root = x;
x->parent = NULL;
S->_size = x->size();
_size -= S->size;
return S;
}
//删除子树 释放空间
template <typename T>
int removeTreeByRootNode(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
if (x == NULL) return 0;
int n = 1 + removeTreeByRootNode(x->lchild) + removeTreeByRootNode(x->rchild);
delete x;
return n;
}
遍历操作
见源代码
显示接口 display
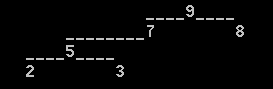
该函数可以在命令行界面下显示一棵二叉树。效果如图
显示时,结点的水平顺序就是中序遍历时结点的顺序,而垂直高度通过层次遍历得到。思路很简单,具体实现有点繁琐。见 二叉树的图形化显示
二叉搜索树
从二叉树派送而来,重写或增加 search 、insert和remove接口
search
二叉搜索树查找算法,该函数同时记录了查找结果的父节点,记录在hot成员变量中。这样可以用于insert时调用。
#ifndef MY_BST_H
#define MY_BST_H
#include "Bintree.h"
template <typename T>
class BST : public BinTree<T>
{
public:
BST();
virtual BinNodePosi(T) search(const T &);
virtual BinNodePosi(T) insert(const T &);
virtual bool remove(const T &);
BinNodePosi(T) removeAt(BinNodePosi(T) x);
protected:
using BinTree<T>::_root;
using BinTree<T>::_size;
BinNodePosi(T) _hot; //parent of (x returned by search)
void transplant(BinNodePosi(T) p, BinNodePosi(T) c); //move single node c to p
void connect34(BinNodePosi(T) t1, BinNodePosi(T) t2, BinNodePosi(T) t3, BinNodePosi(T) st1, BinNodePosi(T) st2, BinNodePosi(T) st3, BinNodePosi(T) st4);
};
template <typename T>
BST<T>::BST()
{
_hot = NULL;
}
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) searchIn(BinNodePosi(T) root, const T & e, BinNodePosi(T) & hot)
{
BinNodePosi(T) x = root;
hot = 0;
while (x != NULL)
{
if (e == x->data)
return x;
hot = x;
if (e < x->data)
x = x->lchild;
else
x = x->rchild;
}
return x;
}
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BST<T>::search(const T & e)
{
return searchIn(_root, e, _hot);
}
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BST<T>::insert(const T & e)
{
BinNodePosi(T) p = BST<T>::search(e);
if (p != NULL && p->data == e) //already exist
{
return p;
}
BinNodePosi(T) x = new BinNode<T>(e, _hot);
if (_hot == NULL) //empty tree
{
_root = x;
}
else //insert as a leaf
{
if (e < _hot->data)
_hot->lchild = x;
else
_hot->rchild = x;
}
++_size;
this->updateHeightAbove(x);
return x;
}
//the called function should modify the lchild and rchild of c
//meanwhile, children node of p not changed
template <typename T>
void BST<T>::transplant(BinNodePosi(T) p, BinNodePosi(T) c)
{
if (p == _root)
{
_root = c;
if (c)
c->parent = 0;
return;
}
if (p->parent->lchild == p)
p->parent->lchild = c;
else
p->parent->rchild = c;
if (c) c->parent = p->parent;
}
//删除结点x 若有左右孩子,与中序后继交换再删
//返回实际删除的结点的替代者指针 _hot指向删除后实际删除节点替代者的父节点
template <typename T>
BinNodePosi(T) BST<T>::removeAt(BinNodePosi(T) x)
{
BinNodePosi(T) suc;
if (!x->lchild) //x has no lchild, just use rchild to replace x,including rchild==NULL
{
suc = x->rchild;
_hot = x->parent;
transplant(x, x->rchild);
}
//has lchild
else if (!x->rchild) //no rchild ,move lchild to x
{
suc = x->lchild;
_hot = x->parent;
transplant(x, x->lchild);
}
else //two children
{
BinNodePosi(T) p = x->succ();
//p has no lchild
suc = p->rchild;
_hot = p->parent;
T tmp = x->data;
x->data = p->data;
p->data = tmp;
transplant(p, p->rchild);
}
--_size;
this->updateHeightAbove(_hot);
return suc;
}
template <typename T>
bool BST<T>::remove(const T & e)
{
BinNodePosi(T) x = search(e);
if (!x) return false;
removeAt(x);
delete x;
return true;
}
template <typename T>
void BST<T>::connect34(BinNodePosi(T) t1, BinNodePosi(T) t2, BinNodePosi(T) t3, BinNodePosi(T) st1, BinNodePosi(T) st2, BinNodePosi(T) st3, BinNodePosi(T) st4)
{
t1->lchild = st1; if (st1) st1->parent = t1;
t1->rchild = st2; if (st2) st2->parent = t1;
t3->lchild = st3; if (st3) st3->parent = t3;
t3->rchild = st4; if (st4) st4->parent = t3;
t2->lchild = t1; t1->parent = t2;
t2->rchild = t3; t3->parent = t2;
this->updateHeightAbove(t1);
this->updateHeightAbove(t3);
}
#endif
BST.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "BST.h"
template <typename T>
class MyPrint
{
public:
void operator()(T const &e)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
};
int main()
{
// MyPrint<int> visit;
BST<int> b;
// b.insert(8);
// b.insert(3);
// b.insert(7);
// b.insert(9);
// b.insert(11);
// b.insert(5);
// b.insert(51);
// b.insert(2);
// b.insert(1);
// b.insert(88);
// b.insert(64);
// b.insert(67);
// b.travIn(visit);
// cout << endl << b.height() << endl;
// b.remove(51);
// b.travIn(visit);
// cout << endl << b.height() << endl;
// cout << endl;
// b.remove(67);
b.insert(7);
b.insert(6);
b.insert(5);
b.insert(4);
b.insert(3);
b.insert(2);
b.insert(1);
b.display();
cout << endl << endl;
return 0;
}
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏