一般的二叉搜索树的高度并没有得到有效限制,在极端情况下,他甚至可以退化为一个链表。而对树高进行限制以达到O(logn)高度的二叉搜索树,又称为平衡搜索树。AVL树是最先发明的自平衡二叉查找树,它的名字来源于它的发明者 G.M. Adelson-Velsky 和 E.M. Landis 。
平衡搜索树因为树高控制在O(logn)的范围内,查找操作用时O(logn)。进行插入和删除操作时,可能会破坏树的平衡性质,需要进行重平衡操作(rebalance)。
定义
首先定义结点的平衡因子,等于左子树高度减去右子树高度。AVL树的每个结点的平衡因子取值只有-1, 0, 1三种取法,也就是说任意结点的左右孩子高度差不超过一。
AVL树的高度
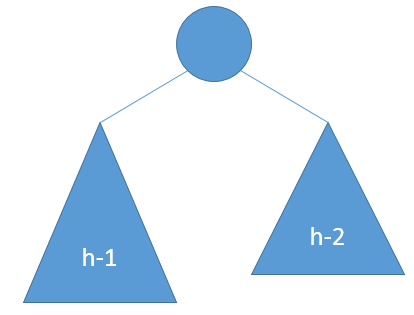
为了说明AVL树的高度和结点数的关系,我们从相反的角度,考虑高度为h的AVL树最少包含多少个结点。
令高度为h的AVL树包含的最少结点是T(h),则高度为h-1的AVL树最少结点是T(n-1),高度为h-2的AVL树最少结点是T(n-2)。接下来用递归的思想来考虑如何得到一棵高度h的AVL树。
显然,树的左右孩子也必须是AVL树。由于总高度为h,因此左孩子或右孩子中的较大者高度为h-1,另一个孩子高度为h-1或h-2 ,由于我们要计算最少结点数,另一个孩子高度取h-2
由此得到递推关系式: T(h) = T(h-1) + T(h-2) + 1 ,初始条件 T(1) = 1 , T(2) = 2
对两边同时+1 ,得 T(h) + 1 = T(h-1)+1 + T(h-2) + 1
令S(h) = T(h) + 1 , S(h) = S(h-1) + S(h-2) ,S(1) = 2, S(2) = 3
对比斐波那契数列 0 1 1 2 3 5
可得 S(h) = F(h+2)
T(h) = F(h+2) – 1
而F(n)的通项中n在指数上,由此可得,节点数为n时,高度为O(logn)量级。
查找
AVL的查找可以直接使用BST的查找,算法不变。由于树高得到控制,查找时间复杂度为O(logn)
插入
插入后失去平衡的情况有4种,重平衡的过程也可以通过单旋和双旋来完成。
首先来看简单的单旋:
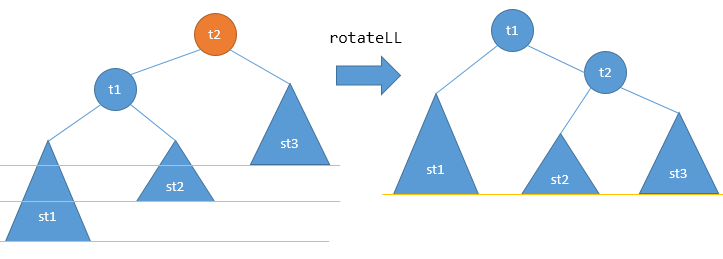
左左情况 rotateLL
某结点因为其左孩子的左子树插入导致失衡,在这里叫做rotateLL过程。
代码如下
template <typename T>
void AVL<T>::rotateLL(BinNodePosi(T) t1, BinNodePosi(T) t2)
{
//t2 --> st2
t2->lchild = t1->rchild;
//st2 --> t1
if (t1->rchild)
t1->rchild->parent = t2;
//t1 --> t2
t1->rchild = t2;
//父节点 --> t1(树根情况)
if (t2->parent == NULL)
{
t1->parent = NULL;
this->_root = t1;
t2->parent = t1;
return;
}
//t1 --> 父节点
t1->parent = t2->parent;
//父节点 --> t1(非树根)
if (t2->parent->lchild == t2)
t2->parent->lchild = t1;
else
t2->parent->rchild = t1;
//t2 --> t1
t2->parent = t1;
}
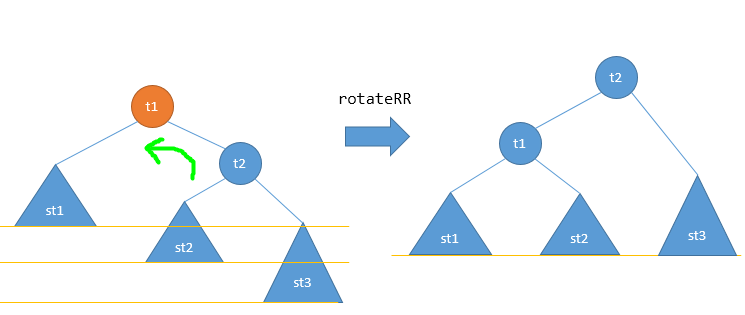
右右情况 rotateRR
某结点因为其右孩子的右子树插入导致失衡,在这里叫做rotateRR过程。
代码如下
template <typename T>
void AVL<T>::rotateRR(BinNodePosi(T) t2, BinNodePosi(T) t1)
{
//t1 --> st2
t1->rchild = t2->lchild;
//st2 --> t1
if (t2->lchild)
t2->lchild->parent = t1;
//t2 --> t1
t2->lchild = t1;
//父节点 --> t2(树根)
if (t1->parent == NULL)
{
this->_root = t2;
t2->parent = NULL;
t1->parent = t2;
return;
}
//t2 --> 父节点
t2->parent = t1->parent;
//父节点 --> t2(非树根)
if (t1->parent->lchild == t1)
t1->parent->lchild = t2;
else
t1->parent->rchild = t2;
//t1 --> t2
t1->parent = t2;
}
左右情况
某结点的左孩子的右子树插入导致失衡。此时需要进行两次单旋。
右左情况
某结点的右孩子的左子树插入导致失衡。此时需要进行两次单旋。
此情况与左右情况对称,此处略去。
使用旋转重平衡
template <typename T>
void AVL<T>::insertFixUp(BinNodePosi(T) p)
{
BinNodePosi(T) q;
q = tallerChild(p);
q = tallerChild(q);
if (p->lchild && q == p->lchild->lchild)
{
rotateLL(q->parent, p);
}
else if (p->rchild && q == p->rchild->rchild)
{
rotateRR(q->parent, p);
}
else if (p->lchild && q == p->lchild->rchild)
{
rotateRR(q, q->parent);
this->updateHeightAbove(q->lchild);
rotateLL(p->lchild, p);
}
else
{
rotateLL(q, q->parent);
this->updateHeightAbove(q->rchild);
rotateRR(p->rchild, p);
}
this->updateHeightAbove(p);
}
3+4重构
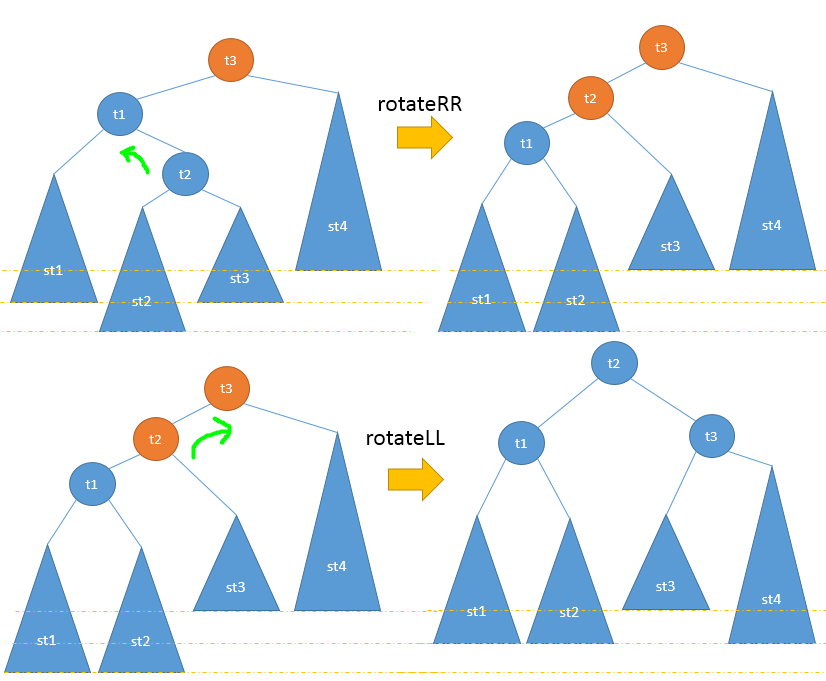
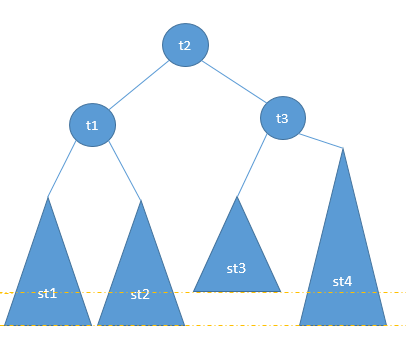
上面通过旋转来使树恢复平衡的过程比较繁琐。实际上可以通过观察发现,不管怎么旋转,调整后的树仍然要满足中序遍历下的大小关系。
例如上面的左右情况,旋转最终的结果的拓扑连接总是下图这样:
因此,直接将这3个结点,4个子树连接成上图的样子,既方便又明了。
template <typename T>
void AVL<T>::insertFixUp2(BinNodePosi(T) p)
{
BinNodePosi(T) q;
BinNodePosi(T) mid;
mid = tallerChild(p);
q = tallerChild(mid);
BinNodePosi(T) par = p->parent;
enum {ROOT, LEFT, RIGHT} ptoc;
if (p->parent)
{
if (p == p->parent->lchild)
ptoc = LEFT;
else
ptoc = RIGHT;
}
else
ptoc = ROOT;
BinNodePosi(T) t1;
BinNodePosi(T) t2;
BinNodePosi(T) t3;
BinNodePosi(T) st1;
BinNodePosi(T) st2;
BinNodePosi(T) st3;
BinNodePosi(T) st4;
if (p->lchild && q == p->lchild->lchild)
{
t1 = q;
t2 = q->parent;
t3 = p;
st1 = q->lchild;
st2 = q->rchild;
st3 = mid->rchild;
st4 = p->rchild;
}
else if (p->rchild && q == p->rchild->rchild)
{
t1 = p;
t2 = mid;
t3 = q;
st1 = p->lchild;
st2 = mid->lchild;
st3 = q->lchild;
st4 = q->rchild;
}
else if (p->lchild && q == p->lchild->rchild)
{
t1 = mid;
t2 = q;
t3 = p;
st1 = mid->lchild;
st2 = q->lchild;
st3 = q->rchild;
st4 = p->rchild;
}
else
{
t1 = p;
t2 = q;
t3 = mid;
st1 = p->lchild;
st2 = q->lchild;
st3 = q->rchild;
st4 = mid->rchild;
}
switch (ptoc)
{
case ROOT : _root = t2; break;
case LEFT : par->lchild = t2; break;
case RIGHT : par->rchild = t2; break;
}
t2->parent = par;
connect34(t1, t2, t3, st1, st2, st3, st4);
}
template <typename T>
void AVL<T>::connect34(BinNodePosi(T) t1, BinNodePosi(T) t2, BinNodePosi(T) t3, BinNodePosi(T) st1, BinNodePosi(T) st2, BinNodePosi(T) st3, BinNodePosi(T) st4)
{
t1->lchild = st1; if (st1) st1->parent = t1;
t1->rchild = st2; if (st2) st2->parent = t1;
t3->lchild = st3; if (st3) st3->parent = t3;
t3->rchild = st4; if (st4) st4->parent = t3;
t2->lchild = t1; t1->parent = t2;
t2->rchild = t3; t3->parent = t2;
this->updateHeightAbove(t1);
this->updateHeightAbove(t3);
}
删除
template <typename T>
bool AVL<T>::remove(const T & e)
{
BinNodePosi(T) x = search(e);
if (!x) return false;
removeAt(x);
BinNodePosi(T) p = _hot;
BinNodePosi(T) q;
while (p != NULL)
{
q = p;
p = p->parent;
if (!AvlBalanced(q))
{
insertFixUp2(q);
}
}
return true;
}
 支付宝打赏
支付宝打赏  微信打赏
微信打赏